The integration of digital tools has become imperative across various business sectors. In particular, EDI services are progressively emerging as a standard in trade. This article explores the workings of EDI and elucidates the manifold benefits it brings to businesses.
What is EDI
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) embodies the electronic exchange of business data. Through this technology, companies seamlessly transfer trade, transportation, and other essential data, thereby efficiently managing their business processes.
EDI was introduced in the United States in the second half of the twentieth century. Later, this technology was used in Europe and around the world. This led to the need to standardize documents (in particular, their format, list of mandatory data, etc.). This issue became especially acute with the development of accounting systems. Companies needed not only to comply with trade rules but also to find common technical solutions to simplify data exchange.
Data transfer standards in EDI
Several international standards underpin the functioning of EDI in the trade industry. Key standards include:
- UN/EDIFACT – the UN rules for the electronic exchange of documents for government, trade and transport;
- UN/CEFACT – the standard of the United Nations Center for International Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business;
- GS1 is an international system of standards covering more than 100 countries;
- GS1 EANCOM is an international standard for the retail industry;
- GS1 XML is a standard for EDI messages in supply chains in the GS1 system.
Types of documents in EDI
EDI services standardize over 100 types of documents used in trade, logistics, and various industries. Most often, clients exchange the following EDI documents:
- product catalog (PRICAT) – an electronic list of goods containing detailed data on them: product code, description, price, size, weight, color, expiration date, etc;
- order (ORDERS) – a document with detailed information about goods or services ordered from a supplier (quantity, price, date, delivery address, etc.);
- order response (ORDRSP) – a document stating that the supplier confirms or does not confirm the delivery of the ordered items in full or in part;
- shipment notification (DESADV) – an electronic document containing accurate data on the goods that will be shipped from the warehouse and will go to the warehouse;
- waybill (DELNOT) – an electronic document certifying the transfer of goods from the customer to the recipient or carrier and signed by the CEP. There is also another popular format of invoices on the Ukrainian market – COMDOC. The Vchasno.EDI service supports both formats of these electronic documents;
- Receipt of acceptance (RECADV) – an electronic message informing the supplier of the actual products received;
- invoice (INVOIC) – an electronic invoice for payment for goods. It contains customer details, order numbers and dates, product names, price, etc;
- Inventory Report (INVRPT) – an electronic message containing information about the stock of goods in a warehouse or store, which allows you to better plan the next delivery.
How EDI works
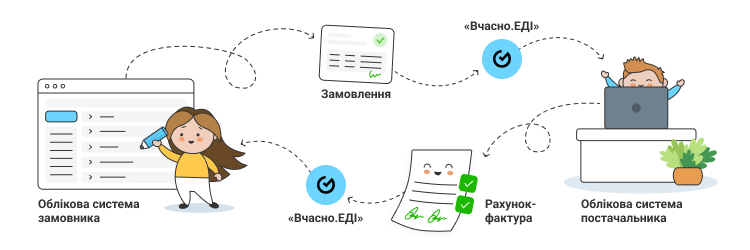
Electronic data flows between the software platforms of the customer and the supplier. An EDI provider acts as an intermediary between them.
The commercial information exchanged between the participants can be in various forms (spreadsheets, text documents, databases, etc.). The EDI system structures this information and sends it in a standardized format. This allows the recipient to extract the data they need from the document and upload it to their accounting system.
Trading partners exchanging data in EDI format must comply with applicable laws and regulations. In particular, special requirements apply to source documents, as they are legally significant. EDI platforms standardize all primary documents that accompany the supply chain. To make a document legally binding, exchange participants sign documents in the EDI service with a qualified electronic signature (QES).
Advantages of using EDI
EDI has many advantages over the exchange of paper documents. Let’s consider them in the example of the Vchasno.EDI service.
Speed of information exchange. When exchanging paper primary documents, networks spend a lot of time printing, sending by courier, waiting for signed documents, etc. If one of the parties makes mistakes, the time for processing and sending doubles. It takes a few seconds to send an electronic invoice or other document to Vchasno.EDI. Thus, the documents are completed even before the goods are delivered to the customer.
It takes a few seconds to send an electronic invoice or other document to Vchasno.EDI. Thus, the documents are completed even before the goods are delivered to the customer.
The ability to control business processes. From the order to the registration of the tax invoice, there are 3 more intermediate documents that are issued at the time of checking the warehouse balances, shipment, and acceptance. At each of these stages, you can check for logistics problems and solve them in time.
Integration capabilities. Retail chains can fully integrate Vchasno.EDI with its accounting system work in a convenient environment. Vchasno.EDI has developed integration modules for suppliers.
Convenient archive storage. A large volume of primary documents requires a large archive storage space and a certain number of archivists. Vchasno.EDI stores documents in a cloud archive. The user of the service can quickly find the desired document by date, EDRPOU code, or other details.
Learn more about Vchasno.EDI
Get acquainted with all the features of Vchasno.EDI and start using it.







