The use of EDI platforms is gradually becoming a standard in the work of retail chains. In this article, we will discuss how the EDI system works in Ukrainian trade and what benefits it provides to companies.
Document workflow in retail chains
Business processes in retail involve a constant workflow of documents. Retail chains exchange purchase orders, invoices, delivery notes, and other documents with suppliers on a daily basis.
If partners keep sending paper documents to each other, it causes a lot of inconvenience:
- Company employees have to manually transfer all the data to their own accounting systems;
- suppliers send documents along with goods, where they can get lost or damaged on the way;
- in case of discrepancies during the acceptance of goods, employees have to re-draft and sign documents;
- companies need to store an archive of documents.
Under such conditions, companies spend a lot of time on paperwork. As a result, the goods may not reach the supermarket shelves on time, and the chain may lose potential profits.
In addition, the goods documents become the basis for tax reporting. If the archive of documents is large, it can be difficult for an accountant to quickly find the right document at the request of a tax inspector. To avoid such inconveniences, more and more retail chains are switching to EDI services for exchanging data with suppliers.
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) is an automated process of transferring structured data between computer systems.
EDI — electronic data interchange system
The EDI system helps retail chains to organize business processes with suppliers: manage financial flows and supply chains.
The system uses standard data exchange formats (EANCOM, EDIFACT, ANSI X12, etc.) to enable companies around the world to exchange EDI documents. As a result, companies exchange information quickly and smoothly and fully automate the supply of goods.
For example, to order goods from a supplier, a retailer creates an order file and indicates the date of the order, product IDs and names, delivery location, and other necessary information. The EDI platform then converts the data into a standard format and sends the document to the supplier. The supplier receives the document in the EDI service and sends back documents (e.g., order confirmation) to the retailer in the same way.
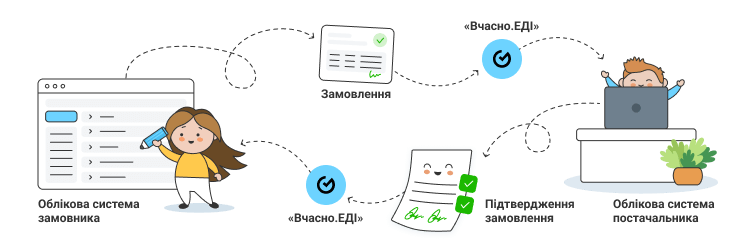
Electronic data interchange (EDI) services fully automate the goods supply process. All the data required for the exchange of messages between the chain and the supplier are made in a single format. As a result, all companies switching to EDI can conveniently interact within the service and quickly exchange messages.
Benefits of EDI system implementation
EDI was invented as an alternative to a paper-based document exchange. However, a significant number of retailers still exchange paper documents with suppliers.
Retail practice has shown the advantages of EDI services. The main ones are:
Time saving. Companies exchanging paper documents spend a lot of time preparing invoices and bills, processing orders, and entering data into the accounting system. EDI platforms automate routine processes and save time and efforts for employees.
Usually, a retail employee processes one order manually in 30 minutes, while in EDI it takes 5 minutes. If a store creates 200 orders in a month, using EDI saves 84 hours of working time. The larger the retail chain, the greater the savings.
EDI also saves time on sending documents. Retailers can quickly make business decisions and address supply chain disruptions.
Less errors. With automatic processing in EDI services, retailers avoid mistakes. More accurate document preparation during the supply of goods allows retailers and suppliers to avoid tax fines and lawsuits.
Security. EDI services effectively protect user data from unauthorized access and ensure secure storage of documents. For example, Vchasno.EDI stores all data on Amazon servers, which are among the most reliable in the world.
Extensive integration capabilities. EDI platforms are integrated with many accounting systems. Therefore, employees do not need to enter data manually.
In EDI documents, all data is clearly structured. It is easy to select the data that is needed for goods accounting and other logistics processes.
Vchasno.EDI service implementation experience
More than 80 Ukrainian retail chains exchange documents with suppliers using the Vchasno.EDI service. For Ultramarket, for example, the transition to EDI was just a part of a larger project aiming to switch to electronic document workflow.
First, we arranged an internal electronic document workflow using Vchasno.EDI. The next thing we did was to implement Vchasno.EDI to automate the ordering of goods. Now we are transferring invoices, returns, and other processes to EDI.
EDI and ODE services are also widely used by companies that work with corporate clients. They need to sign legally significant documents (contracts, agreements, invoices, etc.) that enable cashless payments for goods. Among others, Rozetka uses the Vchasno.EDI and Vchasno.ODE services for such purposes.
For us, cooperation with Vchasno is not limited to just trading activities. In addition to the marketplace, we have b2b clients who buy goods by bank transfer. With these clients, we sign electronic contracts, additional agreements, invoices, statements of provided services, and other important documents.
Getting started with Vchasno.EDI
The Vchasno.EDI service enables trading companies to address many current challenges:
- to automate the entire supply chain of goods;
- to work with all partners in a user-friendly interface;
- to receive orders on time;
- to avoid errors in documents and correct them in a timely manner.
Learn more about Vchasno.EDI
Get acquainted with all the features of Vchasno.EDI and start using it.
Frequently asked questions about EDI
What is the difference between EDI and electronic document workflow services?
How does Vchasno.EDI integrate with accounting systems?
What documents can you exchange in EDI services?

Popup title

Thank you! We will contact youas soon as possible